Voice AI That Powers
Smarter Hiring Decisions
Pioneered by voice technology experts with decades of experience, Aecho transforms recruitment with AI-powered voice analysis that evaluates candidates more accurately and efficiently than traditional methods.
Pioneers in Voice Technology
With decades of experience in voice AI, our team has:
- Invented a portable reading system for the blind in the 1990s
- Created the first voice recognition product for consumers in the 1980s
- Built Arizona's voice-accessed traffic and tourism system
- Authored the definitive book on Voice XML and voice technology
The Problem We're Solving
Traditional recruiting takes 5-6 weeks just to screen candidates
Companies spend $500B - $1T per year on bad hires
89% of hiring failures are due to poor soft skills assessment
Introducing Aecho Recruiter
The Tesla Autopilot for Recruitment
What Tesla did by combining cameras and sensors for autonomous driving, Aecho is doing by combining voice analysis and fraud detection for autonomous recruiting.
Reduces Time-to-Hire by 95%
From 42 days to less than 1 day
Comprehensive Evaluation
Assesses both technical skills and soft skills
Unbiased Assessment
Language-independent analysis focuses on delivery, not content
Deepfake Proof
Advanced security prevents voice fraud
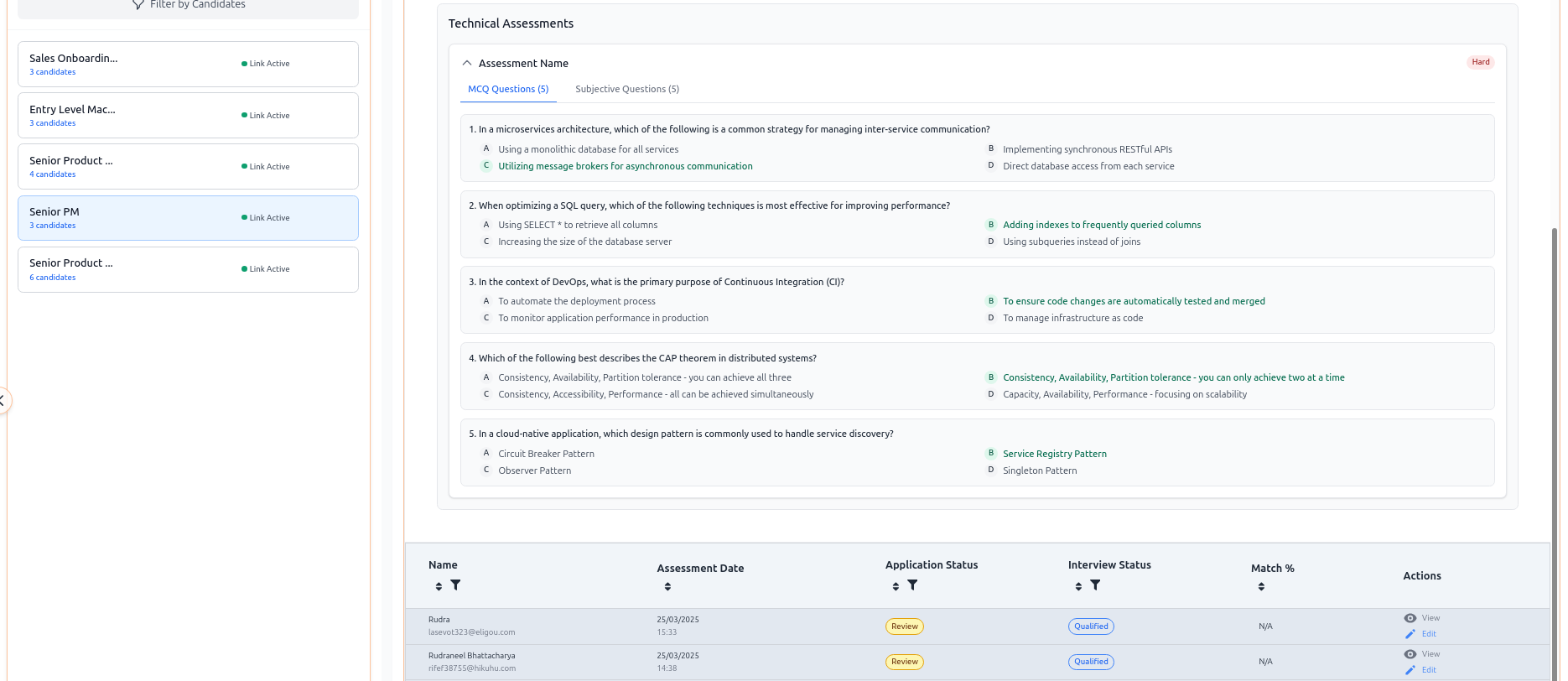
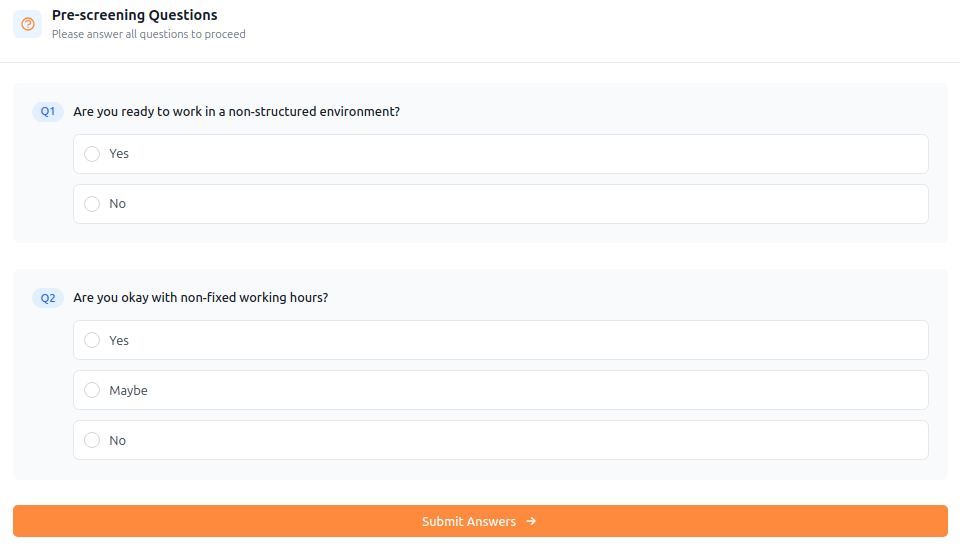
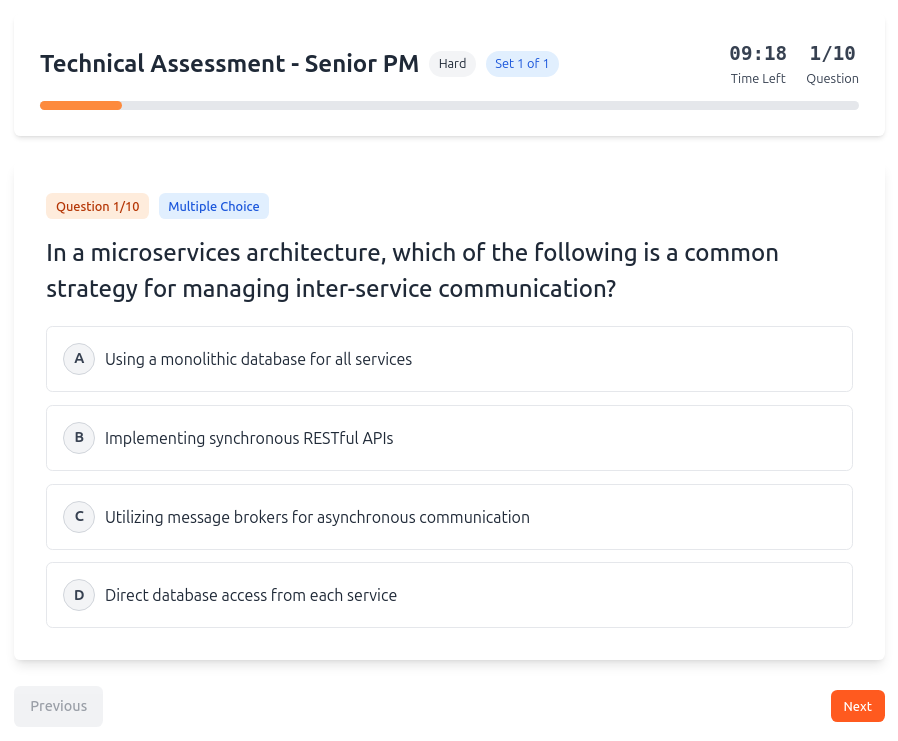
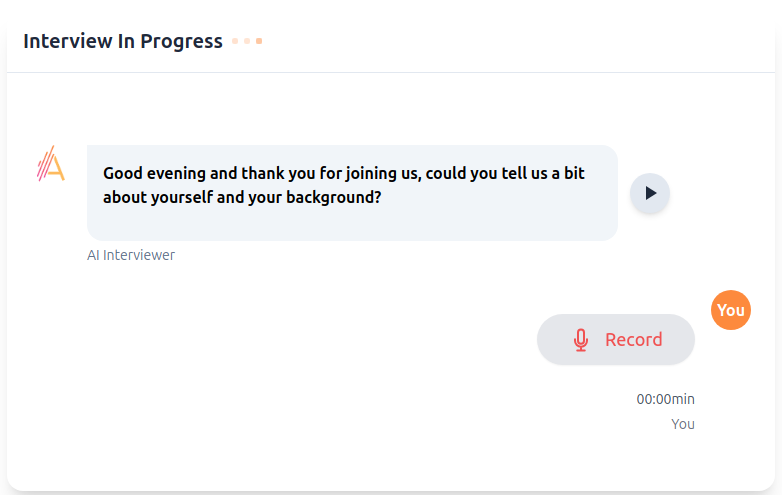
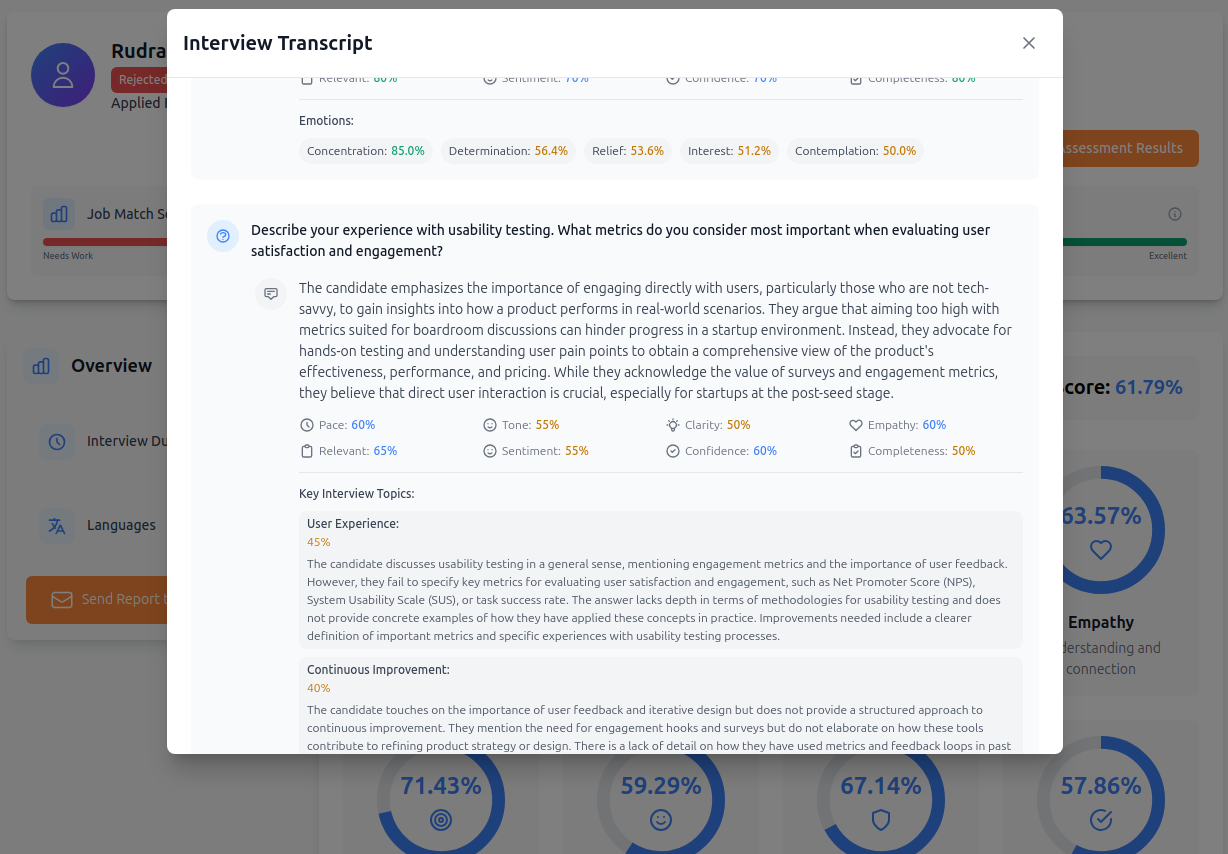
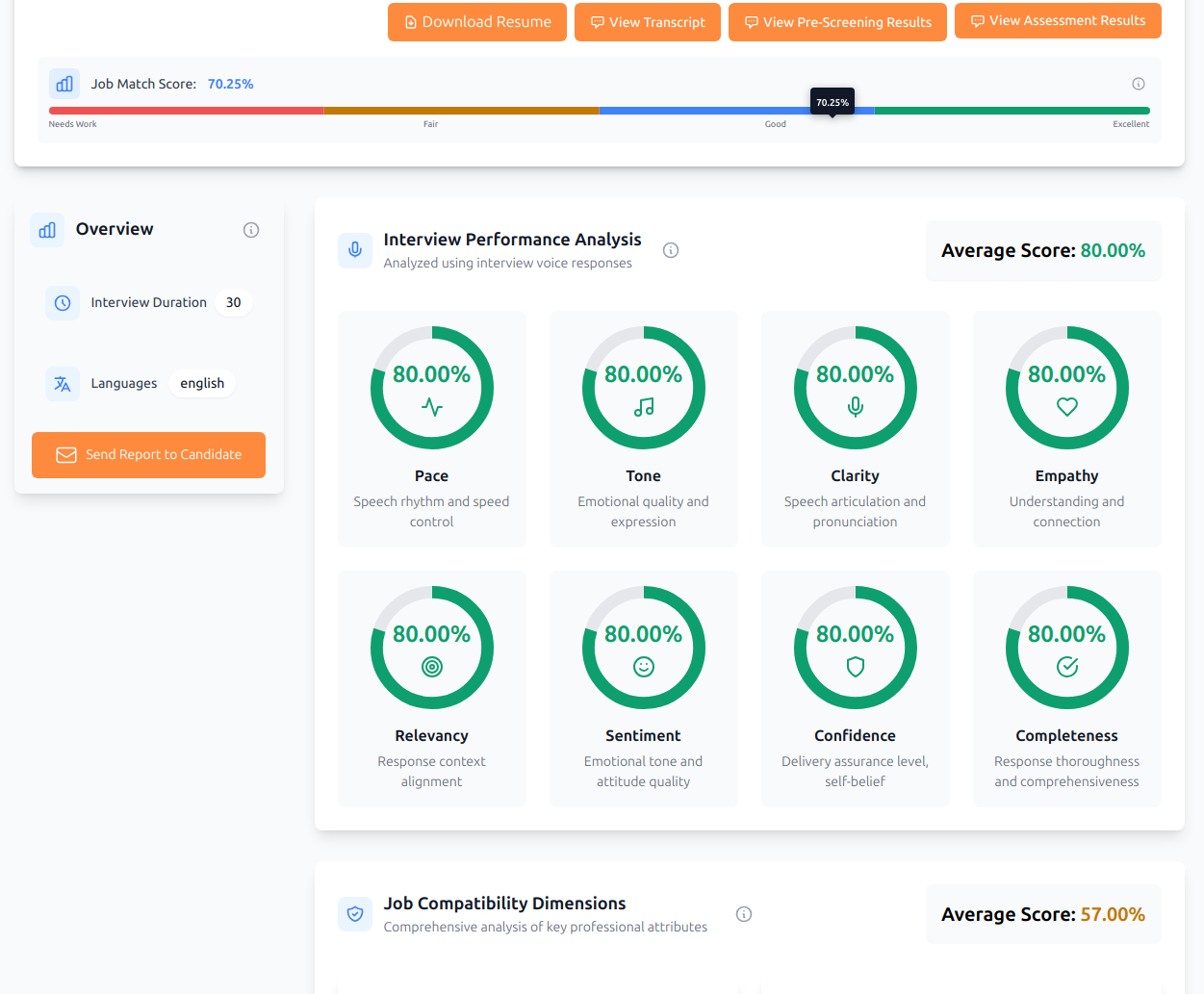
How Aecho Recruiter Works
Interactive AI Interview
Candidates simply click their invite to start the process, uploading their resume, completing assessments followed by the voice interview
AI Analysis
Our AI evaluates over 20 dimensions and 100+ sub-traits through speech patterns, tone, and delivery.
Actionable Insights
Get detailed reports with job compatibility scores (0-100) to make confident, data-driven hiring decisions.
Trusted By Forward Thinking Companies





Strategic Partnerships

Collaborating on advanced voice analysis technology

Powered by Microsoft Azure's secure cloud infrastructure

Accelerating our growth and market reach
Proud Graduate of Peachscore + Dealum Accelerator
We're excited to have graduated from the prestigious Peachscore Accelerator program, which has helped us refine our product and go-to-market strategy.
Learn more about Peachscore
What our Clients Say
Aecho Recruiter has completely transformed our technical hiring process. We've cut our time-to-hire from 6 weeks to just 3 days, and the quality of candidates has actually improved. The voice analysis catches nuances our traditional screening process missed.
Technical Recruiting Director
Fortune 500 Technology Company
The soft skills assessment is what sets Aecho apart. We've reduced our new hire turnover rate by 37% since implementing Aecho Recruiter. The language-independent analysis means we can hire globally without bias, which has opened up incredible talent pools for us.
Head of Talent Acquisition
Global Staffing Agency
Ready to Transform Your Hiring Process?
Join forward-thinking companies using Aecho Recruiter to hire faster, smarter, and with better results.
Subscribe to the Aecho Newsletter for updates, insights, and exclusive offers!
Subscription Successful!
Thank you for subscribing to the Aecho Newsletter. Stay tuned for updates and exclusive offers!
